📚 Computing Point
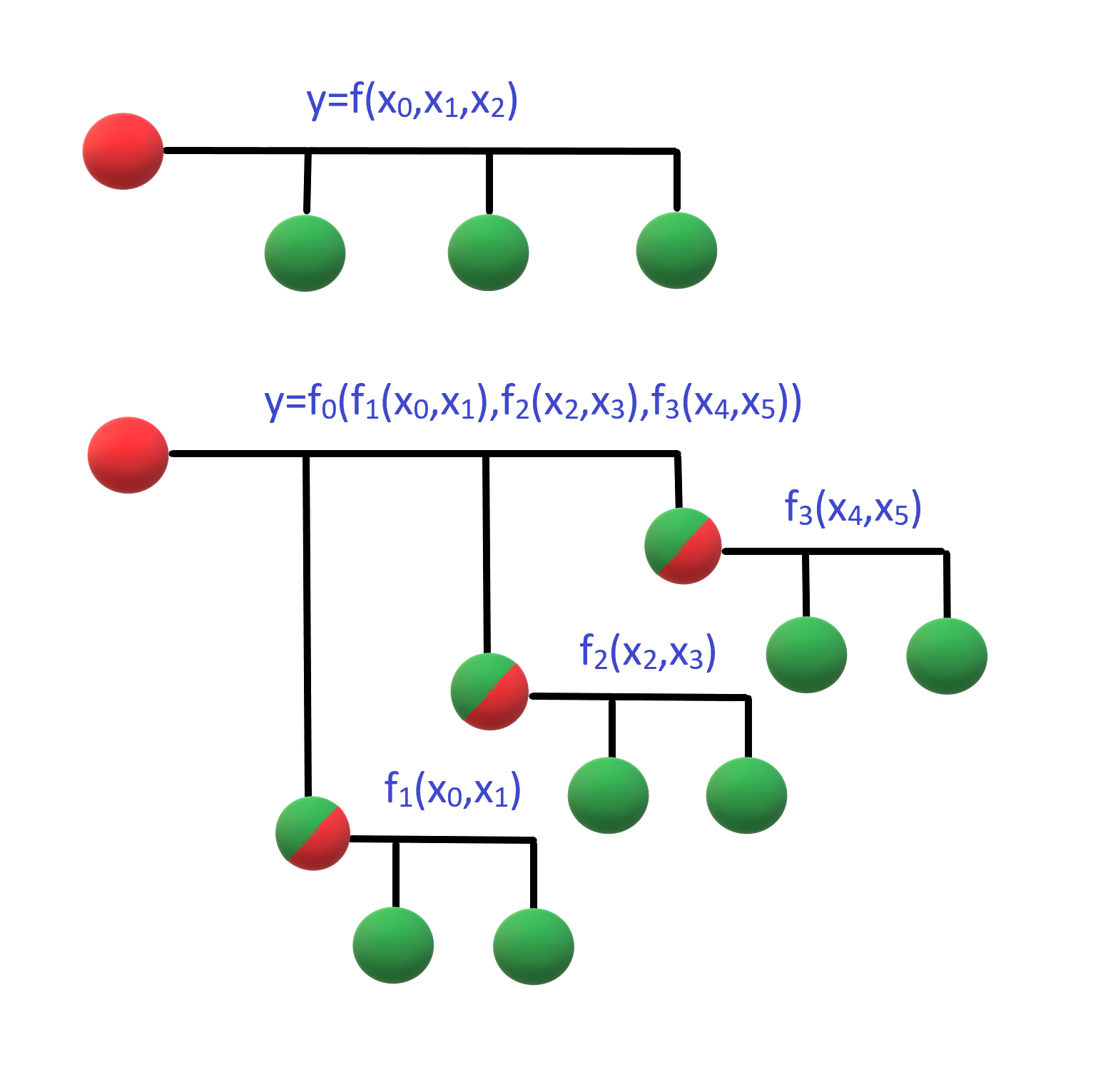 The Thinker™ allows to construct an unlimited hierarchy of math formulae.
Result of one formula, named as computing point and depicted as red or semi-red ball on
the diagram to the right, can serve as an argument to another formula, and so on. Computing
The Thinker™ allows to construct an unlimited hierarchy of math formulae.
Result of one formula, named as computing point and depicted as red or semi-red ball on
the diagram to the right, can serve as an argument to another formula, and so on. Computing
 points are
shown similarly in the project and runtime browsers. Their hierarchy holds assigned
names and allows to collapse and expand branches for convenience. points are
shown similarly in the project and runtime browsers. Their hierarchy holds assigned
names and allows to collapse and expand branches for convenience.
Thinker re-computes full chain of linked formulae on every change of any argument,
thus always providing an actual result. It is an event driven process: when there are no
activations on inputs, all the circuit waits for data delivery. As a general rule, computing
processor doesn't pass a value further across network if the value is found NaN
(not a number). Such policy prevents a computer scheme from accidentally falling into a useless state.
Computing point allows to process any math function, provided that both
arguments and value are real¹ numbers. Endpoint (a point with no
arguments) doesn't require a special math definition because its only role is to accept a value from outside
source. It can be thought as primary argument. However, there are no default functions defined
for computing point at the top and the middle of computing hierarchy. Their function must be referenced
or described within the model.
The key information about the function is a Java class name, including
package name and simple class name.
 It can be seen in the project browser right to the Java logo icon.
For example, here's the name of summing function class in the demo project:
It can be seen in the project browser right to the Java logo icon.
For example, here's the name of summing function class in the demo project:
com.varankin.brains.sample.summator.Sum3.
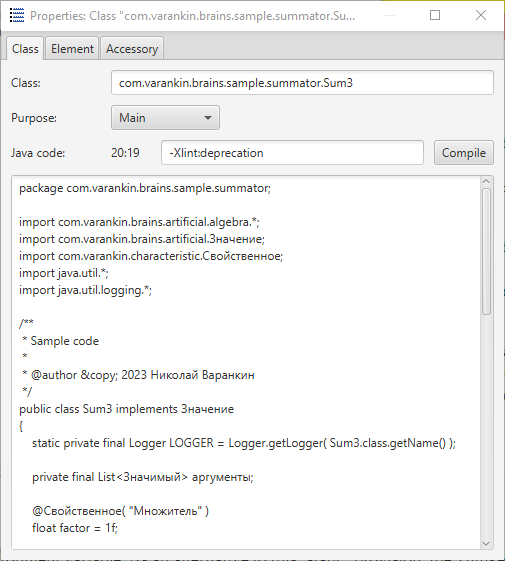 A point, that has only a class name referenced, assumes that Java class code has been supplied
to the model by any method, typically in a
A point, that has only a class name referenced, assumes that Java class code has been supplied
to the model by any method, typically in a jar file mentioned in the CLASSPATH
environment variable. As an alternative to this "static" provision, the Thinker version 2 allows to include
text of Java class code right in the model, either for specific point or within a library. Last variant
allows to reference the class as it would be provided within a jar file. The Thinker uses
embedded Java compiler to generate bytecode of the class. It can be invoked interactively for particular
class, to ensure provided text compiles with no errors. When the model is prepared for runtime, all classes
are compiled automatically.
A minimum requirement for the Java class to be referenced at the point is implementation of a specific
interface. A recommended and simplest one provides a method how to convert an array of arguments
(float[]) into a single value (float), i.e. a convolution. The Thinker
wraps this class into a typical computing solution at runtime. For a more specific requirements a model
can provide a class of more general interface, matched for final point, middle point and endpoint within
computing hierarchy. Provided class can have regular Java dependencies to other Java classes. Custom classes
can also be added to the model. To help Thinker properly resolve class hierarchy, any referenced or provided
class can be assigned a purpose tag.
 A computing point can be enhanced with one or more accessible parameters, to be used in a method that calculates
result. They can be provided with initial value in the model. Java type of the parameter isn't limited
to numeric types. The Thinker applies its own database tools to exchange value representation with
A computing point can be enhanced with one or more accessible parameters, to be used in a method that calculates
result. They can be provided with initial value in the model. Java type of the parameter isn't limited
to numeric types. The Thinker applies its own database tools to exchange value representation with
String type and other Java types. Also, implementation of parameter within
a class has three options: member variable, getter method, and pair of getter and setter methods. Value of parameter
can be viewed and modified at runtime. To be accessible via GUI, parameter within a class code should be annotated
with a dedicated interface. Unannotated, regular class members of any type can be used too.
Every computing point can have a name that differentiates it from other points. Also, this name participates
in sorting of middle computing points and endpoints when they serve as arguments for another point. To have
a name-independent order of arguments, a point can be assigned a specific integer index. It has no requirement to be
a Java array index. A continuous sequence of integers among indices is also just a recommendation. Same index values
serve as a group index. Further sorting within a group is performed by name of the point.
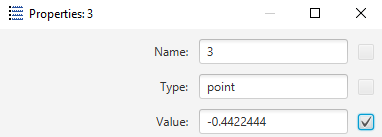 For every point, a pop-up window can be shown, to display and update properties. Runtime properties contain
last value computed by the point. This value automatically updates every time when the point completes next
scheduled calculation. Synchronization can be turned on and off. This form of representation allows to read
an accurate digital value of the signal.
For every point, a pop-up window can be shown, to display and update properties. Runtime properties contain
last value computed by the point. This value automatically updates every time when the point completes next
scheduled calculation. Synchronization can be turned on and off. This form of representation allows to read
an accurate digital value of the signal.
Notes:
- Software versions 1.X and 2.X operate with economy 32-bit floating point numbers,
i.e. Java
float type.
|  The Thinker™ allows to construct an unlimited hierarchy of math formulae.
Result of one formula, named as computing point and depicted as red or semi-red ball on
the diagram to the right, can serve as an argument to another formula, and so on. Computing
The Thinker™ allows to construct an unlimited hierarchy of math formulae.
Result of one formula, named as computing point and depicted as red or semi-red ball on
the diagram to the right, can serve as an argument to another formula, and so on. Computing
 points are
shown similarly in the project and runtime browsers. Their hierarchy holds assigned
names and allows to collapse and expand branches for convenience.
points are
shown similarly in the project and runtime browsers. Their hierarchy holds assigned
names and allows to collapse and expand branches for convenience.
 It can be seen in the project browser right to the Java logo icon.
For example, here's the name of summing function class in the demo project:
It can be seen in the project browser right to the Java logo icon.
For example, here's the name of summing function class in the demo project:
 A point, that has only a class name referenced, assumes that Java class code has been supplied
to the model by any method, typically in a
A point, that has only a class name referenced, assumes that Java class code has been supplied
to the model by any method, typically in a  A computing point can be enhanced with one or more accessible parameters, to be used in a method that calculates
result. They can be provided with initial value in the model. Java type of the parameter isn't limited
to numeric types. The Thinker applies its own database tools to exchange value representation with
A computing point can be enhanced with one or more accessible parameters, to be used in a method that calculates
result. They can be provided with initial value in the model. Java type of the parameter isn't limited
to numeric types. The Thinker applies its own database tools to exchange value representation with
 For every point, a pop-up window can be shown, to display and update properties. Runtime properties contain
last value computed by the point. This value automatically updates every time when the point completes next
scheduled calculation. Synchronization can be turned on and off. This form of representation allows to read
an accurate digital value of the signal.
For every point, a pop-up window can be shown, to display and update properties. Runtime properties contain
last value computed by the point. This value automatically updates every time when the point completes next
scheduled calculation. Synchronization can be turned on and off. This form of representation allows to read
an accurate digital value of the signal.